
واحد مشترک کمکی پژوهش و مهندسی «هوش یار-تواندار» (HT-CSURE)
Hooshyar-Tavandar Common Subsidiary Unit for Research & Engineering
واحد مشترک کمکی پژوهش و مهندسی «هوش یار-تواندار» (HT-CSURE)
Hooshyar-Tavandar Common Subsidiary Unit for Research & Engineeringپیوندهای سایتهای علمی فناوری
پیوندهای علمی مختلف
سایتها و وبلاگهای عمومی
دستههای مطالب
- اخبار و تازه ها 2412
- اخبار فضا 114
- اخبار و تازه های فناوری 2382
- مطالب و مقالات جالب و مفید مرتبط به فناوری 59
- اخبار عمومی فناوری 32
- پیشرفتهای فناوریهای نظامی 106
- اخبار و مطالب مرتبط با فناوریهای مرتبط با ایده ها و اهداف واحد 2356
- اخبار و مطالب روباتیک و هوش مصنوعی 435
- انرژیهای نو و سبز+ روشهای تازه انتقال یا تولید یا ذخیره 225
- سوخت زیستی 38
- انرژی خورشیدی 64
- همجوشی 11
- بازیافت انرژی 24
- باد و جابجایی هوا و سیال 23
- ذخیره انرژی؛ باتری و ... 23
- انرژی حرارتی 8
- سفر و سکونت در جاهای بکر و فضا 271
- روشهای تازه تولید خوراک 341
- ساخت سازه ها و سکونتگاهها 660
- ساختمان هوشمند 72
- ساختمانهای پیش ساخته و جدید 93
- ساخت مسکن و سکونتگاههای ارزان 205
- کاروان 56
- پناهگاه 59
- ساخت مهاجرنشین+مراکز جمعیتی جدید 416
- پرینترهای 3D = سه بعدی 23
- وسایل نقلیه جدید و سازگار با محیط زیست 212
- پژوهشهای پزشکی و زیستی 745
- فناوریهای پوشیدنی 134
- اخبار و مطالب عمومی فناوری اطلاعات 206
- اخبار و مطالب درپیوند با نرم افزار 78
- آینده پژوهی علمی فناوری زیستی 892
- پرواز 134
- پروژه های جاری 126
- اسباب بازی و ماکت 82
- محیط زیست کوچک و بزرگ 536
- مکانیک و مواد 57
- کسب و کار و کارآفرینی 432
- نانو فناوری 10
- ساخت خودرو 38
- ساخت کشتی و شناور 16
- ساخت هواپیما و فضاپیما 20
- مطالب و مقالات متفرقه جالب و مفید 2871
- بهداشت، سلامت، پزشکی 1066
- فرهنگی، اجتماعی، سیاسی و نظامی، مذهبی 2042
- سیاسی و نظامی 888
- فرهنگی 797
- اجتماعی 1491
- مذهبی 625
- آینده پژوهی فرهنگی، اجتماعی، سیاسی، نظامی 1052
- فلسفی 170
- آینده پژوهی مذهبی، انتظار ظهور و آخرالزمان و مرتبط 481
- حقوقی، قضایی 3
- اقتصادی 503
- مطالب درپیوند با پژوهش 16
- روان شناسی 306
- علمی - تخیلی 35
- استوره ای (اسطوره ای) - تاریخی 43
- علوم 113
- ورزش 122
- واحد 32
- مجموعه پیوندها 20
- کاربردی 15
- سرگرمی 102
- آموزشی 92
- الکترونیک 13
- روباتیک 11
- هوش مصنوعی 25
- مکانیک 13
- کامپیوتر (رایانه) 23
- مهندسی عمران و ساختمان 2
- فیزیک 4
- عمومی 20
برگهها
جدیدترین یادداشتها
همه- ریحان؛ ضد دیابت، ضد درد، ضد فشار خون و ضد گاز معده است***
- آیا میدانستید فرآیند پیر شدن از پاها شروع میشود؟
- فیگارو: اروپا برای جنگ با روسیه آماده میشود
- «ایکس» توسط شرکت هوش مصنوعی ایلان ماسک خریداری شد
- بیل گیتس: هوش مصنوعی ۱۰ سال دیگر جایگزین پزشکان و معلمان میشود
- کدام هوش مصنوعی اطلاعات بیشتری از شما را دارد؟(+اینفوگرافی)
- درباره "عمل صالح" و "اصلاح" در سخن حجت الاسلام و المسلمین قرائتی
- ساخت نوعی باتری هستهای بینیاز از شارژ
- هوش مصنوعی برتر متولد میشود؛ نقطه تکینگی
- افرادی که زیاد از ChatGPT استفاده میکنند، دچار وابستگی بالا میشوند
- آیا بدن انسان واقعا برای تمرینات سنگین طراحی شده؟ بازنگری در افسانه تناسب اندام
- «سهروردی» به زبان ساده : فیلسوف ایرانگرایی که تندروها تکفیرش کردند
- دکتر پزشکیان رئیس جمهور: ایران ما زمانی درست خواهد شد که ما تغییر کنیم / باید رفتار، گفتار و ارتباط خود با دیگران را تغییر دهیم
- آشنایی با ویتامینها
- «برتراند راسل» به زبان ساده : مشکل دنیا این است که احمقها بیش از حد مطمئن هستند و عاقلان پر از تردید!
- وایب کدینگ (Vibe Coding) چیست؟ آیا برنامه نویسان به زودی بیکار میشوند؟
- ساخت ورقهای فلزی ۱۰۰۰۰۰ برابر نازکتر از موی انسان!
- میکروصاعقه؛ کلید احتمالی معمای پیدایش حیات در زمین اولیه
- شهادت تسلیت
- ۱۰۰ سریال برتر تاریخ به انتخاب نشریه ایمپایر
- خون افراد درازعمر با بقیه تفاوتهای کلیدی دارد
- هفت آنتیبیوتیک طبیعی را بشناسیم
- هواپیماهای M2 : پرواز بدون بال (+عکس)
- توصیههایی علمی برای جوان ماندن جسم (و پوست) و روح
- ۱۰ شغل پردرآمد آینده که دنیا را تسخیر میکند(اینفوگرافی)
- ورزش کنید تا سالم تر پیر شوید؛ دست کم 150-300 دقیقه فعالیت متوسط در هفته
- دنیای رمزآلود احتمالات؛ چرا «احتمال» احتمالاً وجود ندارد؟
- محققان چینی: هوش مصنوعی با شبیهسازی خودش از خط قرمز عبور کرد
- میلاد مبارک
- تنها شغلهایی که از دست هوشمصنوعی جان سالم به در میبرند، از دید بیل گیتس
- جوانه گندم بخورید تا جوانتر و تن درستتر بمانید
- فناوریهای نو در در پرتاب ماهواره: منجنیق غولپیکری که بدون سوخت، ماهواره را به فضا میفرستد(+عکس)
- ویتامین C، ویتامینی که جوانی را تضمین میکند
- هوش مصنوعی می تواند طول عمر انسان را دو برابر کند
- آقای ملکیان: ریشه فلسفی صلح، اشتراک منافع است + اصلاح و تکمیل مطلب از واحد
- عید مبعث مبارک
- کسی مقیم حریم ترامپ نخواهد ماند!
- مهندس آلمانی۱۲۰ روز زیر آب زندگی کرد (فیلم)
- میلاد مبارک
- میلاد مبارک
- تبدیل سوسکها به سایبورگ تنها در ۶۸ ثانیه!
- لیزر در ابعاد نانومتری ساخته شد***
- «ایلان ماسک» معتقد است که رباتها آینده هوش مصنوعی هستند
- هوش مصنوعی جدید گوگل بهجای شما وبگردی میکند
- مواردی که هرگز نباید به چت بات هوش مصنوعی بگویید!***
- ترفند مأمور سابق سرویس مخفی: چگونه دیگران را به انجام خواسته هایتان ترغیب کنید؟
- تعریف فریب و تدلیس؛ فریب دادن طرف مقابل در انواع معاملات چه آثاری دارد؟
- درباره فریب عرفی «مهریه را کی داده و کی گرفته»
- ماجرای پرمخاطب یک ربات که ۱۲ ربات دیگر را فرمانبردار خود کرده است! (فیلم)
- ساخت نوآورانه بالن فتوولتائیک برای تولید برق خورشیدی
بایگانی
جستجو
کشف جدیدی که ۸ برابر همجوشی هستهای انرژی تولید میکند
کشف جدیدی که ۸ برابر همجوشی هستهای انرژی تولید میکند
به گزارش خبرآنلاین و به نقل از دیجیاتو، منبع این انرژی از همجوشی ذرات زیر اتمی به نام کوارک سرچشمه می گیرد. کوارک ها ذرات اصلی سازنده پروتون و نوترون بوده و به ۶ گروه مختلف تقسیم می شوند.
دانشمندان انواع مختلف کوارک ها را «طعم» نیز می نامند که عبارتند از: بالا، پایین، عجیب، افسون، فوقانی و زیرین (دو مورد آخر گاهی حقیقت و زیبایی نیز نامیده می شوند).
این تیم تحقیقاتی برای بررسی دقیق تر ذرات زیراتمی، اتم ها را در برخورددهندهٔ هادرونی بزرگ (Large Hadron Collider) با سرعت بالا به سمت هم گسیل کرده اند تا کوارک های آنها از یکدیگر جدا شود.
این کوارک ها پس از جداشدن دوباره تمایل به تشکیل پیوندهای جدید دارند که منجر به ایجاد ذراتی به نام «باریون» می شود .
این محققان با تمرکز بر روی کوارک زیرین که سنگین تر از دیگر طعم ها است، دریافتند که باریون های حاصله توانایی تولید ۱۳۸مگا الکترون ولت انرژی خالص را دارند که هشت برابر انرژی تولید شده در همجوشی هسته ای است.
انرژی این فرایند به حدی زیاد است که ممکن است مورد سوء استفاده قرار گیرد، به همین خاطر محققان در ابتدا نسبت به رسانه ای کردن آن تردید داشتهاند.
با این حال آنها تاکید کرده اند که با طراحی و توسعه ابزارهای لازم می توان از این روش برای تولید انرژی پاک و نامحدود بهره برد.
محصول قطب تولید سیب کشور خریدار ندارد (+عکس)
کاغذ خورشیدی شارژر گوشی شد
کرهشمالی برای دور زدن تحریمها به تولید انبوه جلبک رو آورده است

کره شمالی در حال توسعه پروژههای پرورش جلبک به منظور استفاده از این محصول برای مقابله با تحریمهای جامعه بینالملل علیه این کشور است.
به گزارش ایسنا، به نقل از اکسپرس، کرهشمالی بر اساس گزارشها پژوهش برای تقویت امنیت غذایی و انرژی خود را تشدید کرده است. این در حالی است که ارگانیسمهای جلبک میتوانند برای تولید غذا، کود، مواد اولیه صنعتی و سوخت مورد استفاده قرار بگیرند.
وبسایت تحلیلی ۳۸ North متعلق به مخالفان حکومت کره شمالی گزارش داده که صنعت تولید جلبک میتواند به تدریج "تاثیرات منفی تحریمها را هم علیه حوزه تامین انرژی و هم علیه امنیت غذایی" در کره شمالی کاهش دهد.
بر اساس گزارشها، این کشور اقدام به گسترش تاسیسات پژوهشی از جمله حوضچهها و سیستمهای پرورش آبزیان از اوایل سال ۲۰۰۸ تا کنون به همین منظور کرده است.
این تاسیسات در کره شمالی که برای پرورش جلبک کلیدی محسوب میشوند اخیرا پیچیدهتر از قبل شدهاند.
کره شمالی وابستگی فراوانی به واردات سوخت و غذا از خارج دارد و چین به طور تاریخی شریک تجاری اصلی کره شمالی محسوب میشده است. اما پکن اخیرا صادرات نفت پالایش شده خود به کره شمالی را از ابتدای ماه جاری میلادی محدود کرد.
جلبک در صورت فرآوری شدن میتواند میزان بالایی پروتئین داشته باشد و از آن میتوان برای مکمل غذایی و کود استفاده کرد.
وبسایت مخالف ۳۸ North نوشت: جای شگفتی نیست که دولت کره شمالی در حال توسعه هزاران حوضچه باز روستایی برای تولید جلبک و ایجاد سایتهای بزرگتر و پیچیدهتر ظاهرا برای تولید هرچه بیشتر جلبک است.
همین جلبک میتواند ۲۰ درصد چربی داشته و از آن میتوان به عنوان سوخت زیستی استفاده کرد.
Gamma Rays Can Go Past the Limits of Light
Gamma Rays Can Go Past the Limits of Light
Researchers have discovered a way to produce high energy photon beams. This method makes it possible to produce gamma rays in a highly efficient way when compared to today’s technique. The obtained energy is a billion times higher than the energy of photons in visible light. High-intensity gamma rays significantly exceed all known limits of light and will pay the way towards new fundamental studies.
"When we exceed the limit of what is currently possible, we can see deeper into the basic elements of nature. We can dive into the deepest part of the atomic nuclei," says Arkady Gonoskov, a researcher at the Department of Physics at Chalmers University of Technology.
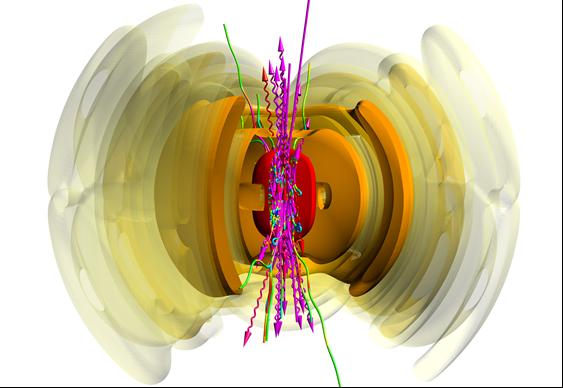
Gamma rays are electromagnetic waves, just like visible light or X-rays, but with much higher energy. The most energetic gamma rays in the world could be created by the help of advanced laser physics. When the laser light is intense enough and all parameters are right, trapped particles (green) could efficiently convert the laser energy (surfaces in red, orange and yellow) into cascades of super-high energy photons (pink). (Arkady Gonoskov)
This new method is the outcome of collaboration is an outcome of collaboration between Chalmers University of Technology in Sweden, Institute of Applied Physics and Lobachevsky University in Russia and the University of Plymouth in the UK. Physicists in different fields have managed to work out the numerical models and analytic estimates for simulating the ultra-strong gamma rays in a new and somehow unexpected way.
In normal cases, if a laser pulse is shot at an object, all the particles scatter. But if the laser light is intense enough and all parameters are right, the researchers found that the particles are trapped instead. They form a cloud where particles of matter and antimatter are created and start to behave in a special and unusual way.
"The cloud of trapped particles efficiently converts the laser energy into cascades of high energy photons - phenomena that is very fortunate. It's an amazing thing that the photons from this source can be of such high energy," says Mattias Marklund, a professor at the Department of Physics at Chalmers.
The discovery is highly relevant for the future large-scale facilities that are currently under development. The most intense light sources on earth will be produced in these research facilities that are as big as football fields.
"Our concept is already part of the experimental program proposed for one such facility: Exawatt Center for Extreme Light Studies in Russia. We still don't know where these studies will lead us, but we know that there are yet things to be discovered within nuclear physics, for example, new sources of energy. With fundamental studies, you can aim at something and end up discovering something completely different - which is more interesting and important," says Arkady Gonoskov.
A paper on this research was published in Physical Review X













